Here is a table of key difference between microsphere and microcapsule according to their size, composition, and release mechanisms.
What is microsphere?
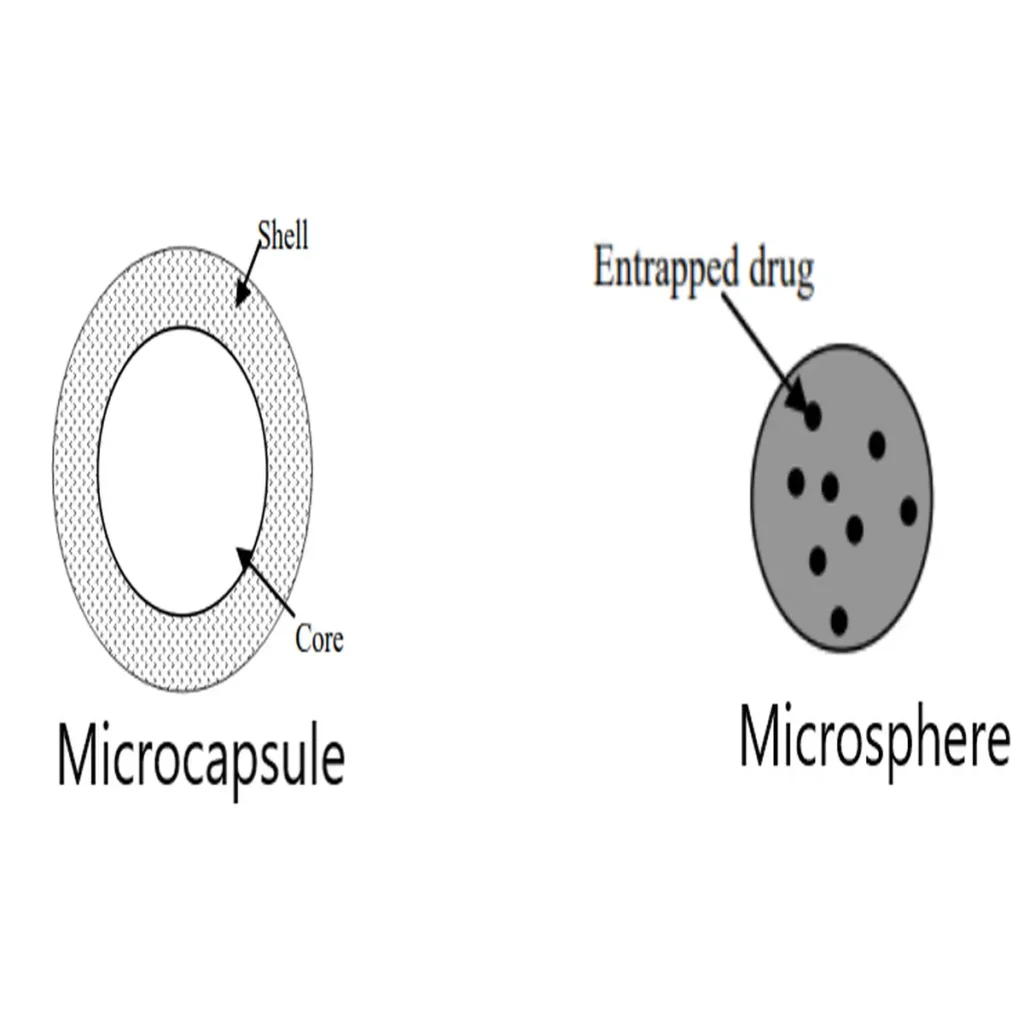
A microsphere is the small spherical particles (1-1000μm) made of biodegradable proteins or synthetic polymers. This has two types: microcapsules (with a distinct capsule wall around the entrapped substance) and micromatrices (where the substance disperses throughout the matrix).
They are used to enhance the bioavailability of conventional drugs and also to reduce side effects.
An ideal microsphere should have followed characteristic,
- High drug concentration.
- Stable formulations with a good shelf-life.
- Controlled particle size.
- Easy dispersion in injectable solutions.
- Controlled, extended drug release.
- Biocompatible with controlled biodegradability.
What is a microcapsule?
A microcapsule is small spheres with a uniform wall enclosing a core. The core contains the material, and the wall is the coating.
An ideal microcapsule has these features:
- High drug incorporation capability.
- Ensures stability and a clinically acceptable shelf-life.
- Provides controlled particle size and dispersibility in injectable solutions.
- Releases the active ingredient in a controlled manner for an extended period.
- Biocompatible with controllable biodegradability.
- Susceptible to chemical modifications.
What are the differences between microsphere and microcapsule?
| Characteristic | Microspheres | Microcapsules |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small spherical particles with a uniform size. | Tiny capsules containing a core material. |
| Composition | Homogeneous material throughout. | Core material surrounded by a shell. |
| Structure | Solid or hollow. | Liquid or solid core surrounded by a shell. |
| Purpose | Controlled release of a substance. | Encapsulation of active ingredients. |
| Applications | Drug delivery, cosmetics, food additives. | Pharmaceuticals, flavors, fragrances. |
| Core Material Release | Diffusion or degradation of the microsphere. | Burst release or sustained release. |
| Shell Material | Polymer-based. | Polymer, protein, lipid or combination. |
| Size Range | Typically in the micrometer range. | Typically, in the micrometer range. |
| Processing Methods | Emulsion, spray drying and solvent evaporation. | Coacervation and interfacial polymerization. |
| Examples | PLGA microspheres and chitosan microspheres. | Gelatin microcapsules and alginate capsules. |
Also read Air suspension technique in microencapsulation. What are Microspheres?
