In analysis, concentration is crucial to prepare compound. Learn different methods of expressing concentration in pharmaceutical analysis.
What is concentration?
Concentration means how much of substance is mixed in with another substance. For example, it is like how much sugar is in a cup of tea or how many chocolate chips are in a cookie dough.
We can define concentration as it refers to the particular amount of a substance present within a specific volume or mass of a solution or mixture.
What are the different methods of expressing concentration?
Basically, solution used for analysis requires for expression of solution concentration.
The actual method of expressing concentration should be always convenient and specific form.
Different methods to measure or express concentration includes:
- Normality (N).
- Molarity (M).
- Molality (m).
- Parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb).
- Percentage (%) concentration measurement.
- Formality (F).
- Molar fraction (χ).
Normality
In pharmaceutical chemistry, normality (N) is a measurement unit of concentration.
It indicates the number of equivalents of a solute dissolved in a liter of solution.
In pharmaceutical analysis, it is defined as the number of equivalent or solute per liter of solution. The formula of normality is:
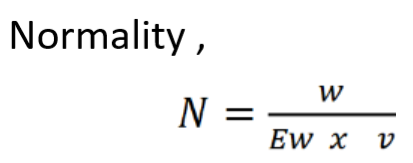
Where,
- N= Normality.
- w= Weight of solute.
- Ew= Equivalent weight of solute.
- v= Volume of solution.
Normality commonly used in acid-base chemistry and redox reactions. For example, a 1 M solution of HCl (hydrochloric acid) would be 1 N because HCl dissociates to give one H+ ion.
Molarity
Molarity (M) is the measurement of concentration of a solute in a solution by expressing the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. For example, you have 0.25 moles of sodium chloride (NaCl) in 1 liter of water. The molarity of the solution is 0.25 M.
The formula is:
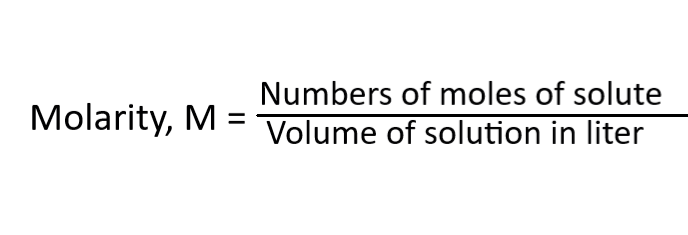
It is a fundamental and straightforward method used to measure concentration. It is useful when the exact molecular weight of solute is known.
Molality
Molality of solution is defined as the number of moles of solute per 1000 gm of solvent. It is expressed as ‘m’.
Unlike molarity, which measures concentration in terms of volume of solution, but molality is expressed in terms of mass of solvent. For example, if you dissolve 0.5 moles of sugar in 1 kg of water, the molality of the solution would be 0.5 m.
The formula is:
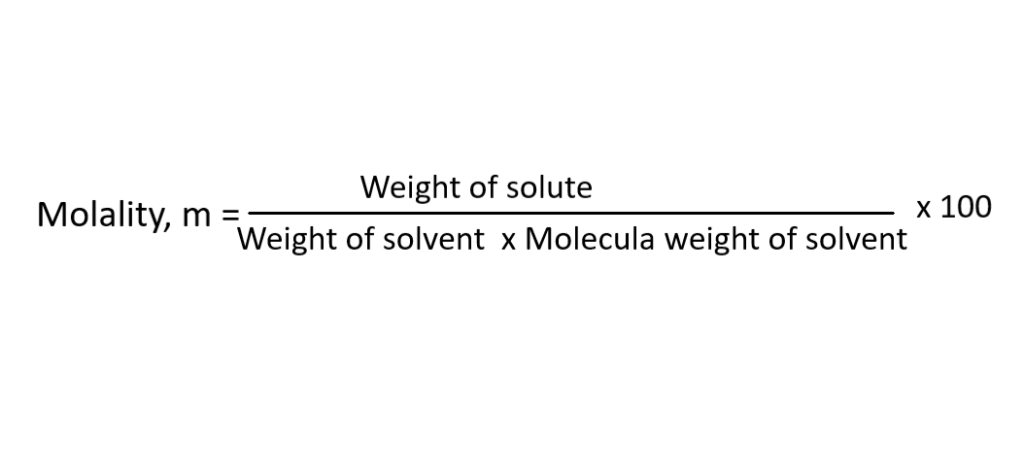
Parts per million or parts per billion
Parts per million also called as ppm. Generally, ppm measures concentration of dilute solution.
The formula for ppm is:
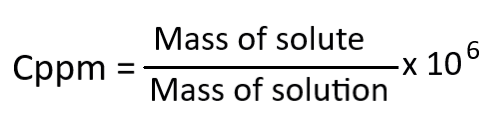
For example, if you have 1 mg of a substance dissolved in 1 liter of water, the concentration would be 1 ppm.
If the dilute solution in a sample is very high the concentration expressed as parts per billion (ppb).
These ppm and ppb both are used to measure concentration of impurities in pharmaceuticals.
Percentage concentration
Percentage concentration expresses the amount of solute present in a solution as a percentage of total solution volume or mass.
We use percent (%) term to express a solution concentration. For different solution, percentage concentration expressed in different ways. Some are:
Mass percentage (w/w %)
It describes the commercial aqueous reagents. The formula is,
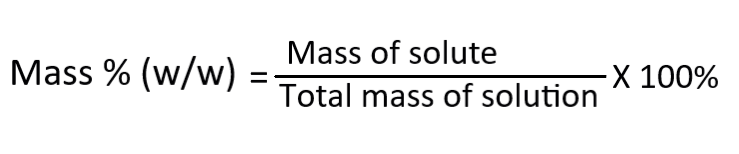
For example, if you have 20 grams of salt in 100 grams of water. The mass percentage of the solution would be (20g / 100g) x 100% = 20%.
Volume percentage (v/v %)
It measures the concentration of solution prepared by diluting pure liquid with another liquid. Formula is,
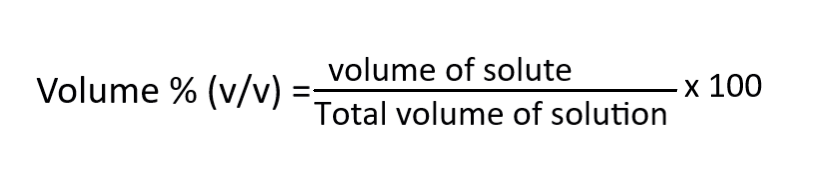
For example, if you mix 20 mL of ethanol with 80 mL of water. The volume percentage of ethanol in the solution would be (20mL / 100mL) x 100% = 20%.
Weight/volume percentage (w/v %)
It expresses the concentration of solution which is prepared by dissolving solids reagents in solvents. The formula is,
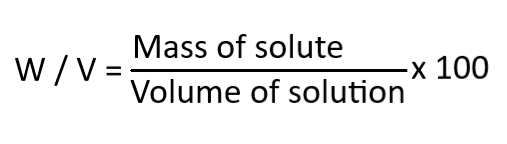
Formality
Formality is the gram formula units present in one liter of solution. It is denoted as F and the formula is,

Molar fraction
Mole fraction is the ratio of the number of moles of a component to the total number of moles in the solution.
It is a dimensionless quantity and is expressed as a fraction. The mole fraction formula is,
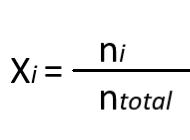
- Xi = molar fraction of component i.
- ni = number of moles of component i.
- n-total = total number of moles of all components in the solution.
For example, you have a solution which contains 0.5 moles of ethanol (C₂H₅OH) and 0.5 moles of water. Now calculate the molar fraction of ethanol in the solution by dividing the moles of ethanol by the total moles of solute. The answer will be 0.5.
What are the factors affecting methods of expressing concentration?
The methods to express the concentration of a solution depends on various factors, including:
Nature of the substance
Based on properties, different substances may require different methods of concentration expression. For example, some substances weight measured accurately, while others substance volume is measured accurately.
Solubility and stability
Solubility and stability of the substance can also impact the choice of concentration expression method. For example, if a substance is highly soluble or unstable, alternative methods is important to determine concentration accurately.
Temperature and pH
Temperature and pH directly impact solution properties, volume, reaction rates and solubility. These factors influence concentration expression methods like molarity.
Why we use methods to express concentration in pharmaceutical chemistry?
Quality control
Pharmaceutical analysis involves testing the quality of raw materials, intermediates and finished products. Expressing concentration allows analysts to ensure that products is in standard form.
Safety and efficacy
Accurate determination of concentration ensures that pharmaceutical products contain the correct amount of active ingredients. This is important for ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals.
Quantify the amount of API
Concentration expression is necessary for developing analytical methods to quantify the amount of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) present in formulations.
MCQ’s
1) The number of moles of solute per liter of solution measurement used in:
- a) Molality
- b) Normality
- c) Molarity
- d) Parts per million
Answer: c) Molarity
2) When is normality commonly used?
- a) In measuring low concentrations.
- b) In acid-base chemistry and redox reactions.
- c) In dilute solutions.
- d) In measuring solubility.
Answer: b) In acid-base chemistry and redox reactions
3) Which concentration measurement is expressed as a percentage?
- a) Molarity.
- b) Parts per million.
- c) Percentage concentration.
- d) Molar fraction.
Answer: c) Percentage concentration
4) What is the formula for molality?
- a) m = moles of solute / liters of solution.
- b) m = moles of solute / grams of solvent.
- c) m = moles of solute / 1000 grams of solvent.
- d) m = moles of solute / moles of solvent.
Answer: c) m = moles of solute / 1000 grams of solvent
FAQ’s
1) Define concentration and give an example.
Ans: Concentration refers to the amount of a substance present within a specific volume or mass of a solution or mixture. For example, the concentration of sugar in a cup of tea.
2) What is normality?
Ans: Normality (N) is a measurement unit of concentration which indicates the number of equivalents of a solute dissolved in a liter of solution.
3) Describe molarity with formula.
Ans: Molarity (M) measures the concentration of a solute in a solution by expressing the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. The formula is: M = moles of solute / liters of solution.
4) How is molality different from molarity?
Ans: Molality (m) measures the number of moles of solute per 1000 grams of solvent, but molarity measures moles of solute per liter of solution.
5) What does ppm stand for?
Ans: PPM stands for parts per million. It measures the concentration of dilute solutions, especially when the concentration is very low.
6) What are the important methods of expressing concentration?
Ans: The basic methods to express concentration are normality, molarity, molality, formality, ppm, percentage concentration, molar fraction etc.
7) Which of the following methods of expressing concentration varies with temperature?
Ans: Molarity.
Also read Different techniques of analysis. Pharmaceutical analysis definition and scope.

