Microencapsulation is a tiny magic trick of science, where we wrap up solids, liquids or even gases within microscopic particles.
How to define microencapsulation?
It is the process of making microcapsules, in which solids, liquids or gases are enclosed within microscopic particles by thin coatings of wall material.
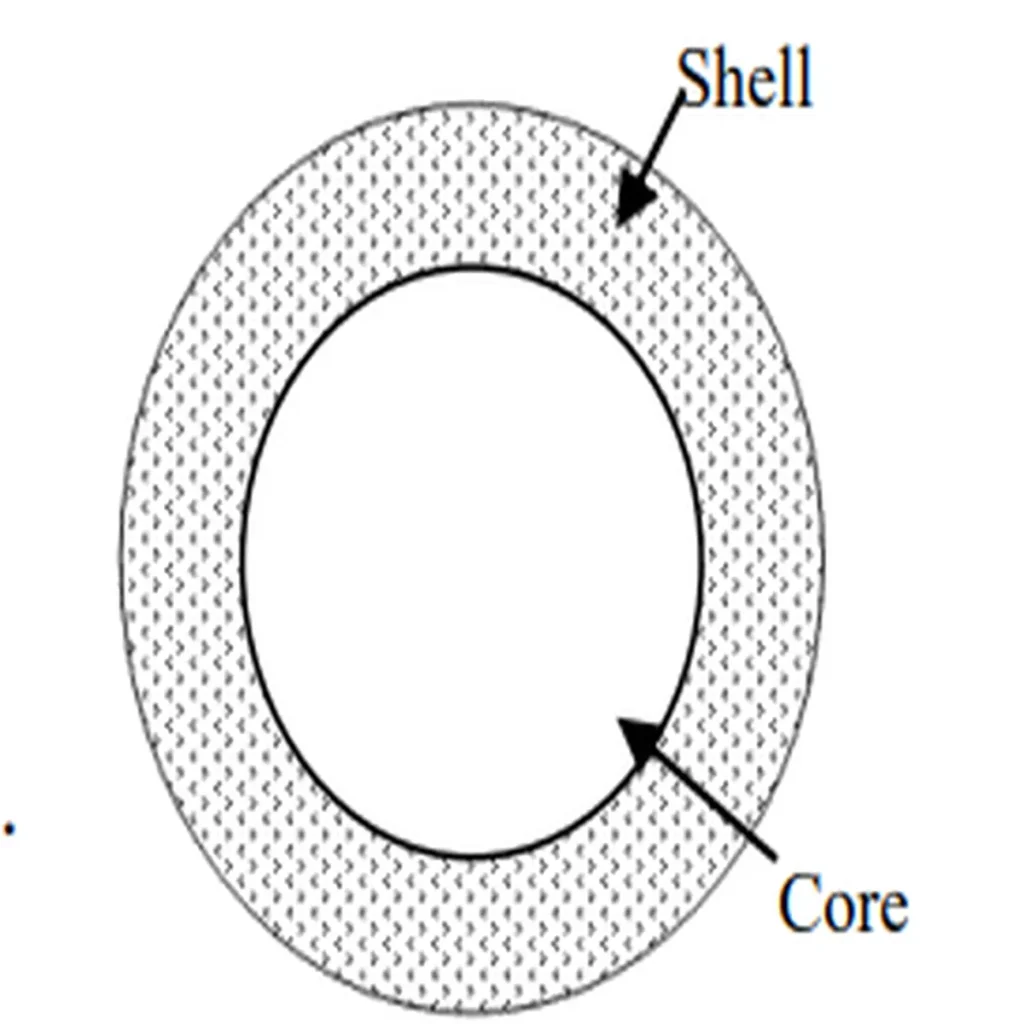
These microcapsules are like tiny spheres, surrounded by a uniform wall. Inside of the wall we have the core, while the outer layer is the coating. The diameter of microcapsules usually ranges between a few micrometers to a few millimeters.
Microencapsulation can also be defined as the process in which individual particles or droplets of solid or liquid material (the core) are surrounded with a continuous film of polymeric material (the coating) to produce microcapsules (in micrometer to millimeter range).
What is core material?
A core material is a stuff we put inside these microcapsules. Here are some properties of core material-
- It should be a liquid or solid.
- Liquid core should be a dissolved or dispersed material.
- It’s made of the same stuff as the coating.
- It should be the drug or the active constituent.
- It should enhance the rate of release.
What is coating material in microencapsulation?
The coating material in microencapsulation is what we put around the core. It should have these properties-
- It does not with the core material.
- It should be compatible with the core material.
- It should keep the core material steady.
- It can release the core material in a controlled way when needed.
- It should form a flexible, brittle, hard and thin coating.
- It should be available in abundance.
- It should be inexpensive.
What are the examples of coating materials?
Gums (gum Arabic, sodium alginate and carrageenan), carbohydrates (starch, dextran and sucrose), celluloses (carboxymethylcellulose and methylcellulose), lipids (beeswax, stearic acid and phospholipids) and proteins: (gelatin and albumin).
Now we will see advantages and disadvantages of microencapsulation.
What are advantages of microencapsulation?
- Makes liquids easier to handle and store.
- Reduces the volatility of substances.
- Prevents incompatibilities in drug combinations.
- Hides unpleasant tastes and odors.
- Reduces irritation caused by some drugs.
- Lessens hygroscopic nature.
- Provides controlled drug release.
- Improves safety with toxic chemicals.
- Enhances flowability of core materials.
- Stabilizes enzymes.
- Allows mixing of incompatible ingredients.
What are the disadvantages?
- It is expensive.
- Not suitable for all materials.
- Coating can be uneven.
- Different techniques are needed for different materials.
- Sensitive drugs may not stay stable.
- Each material needs unique design.
- Release characteristics can be inconsistent.
- Limited safe materials available.
- Mechanical stress can harm the product.
- Not for parenteral applications.
- Scaling up can be difficult in large manufacturing.
Also read What are the advantages of polymers? What are the applications of polymers in ndds?
