Microspheres are the tiny drug carrier for controlled release of drug. Learn definition characteristics and various types.
Microspheres
These are tiny or small round particles having diameter of 1 to 1000μm. They consist of biodegradable proteins or synthetic polymers. Microspheres come in two varieties, microcapsules and micromatrices.
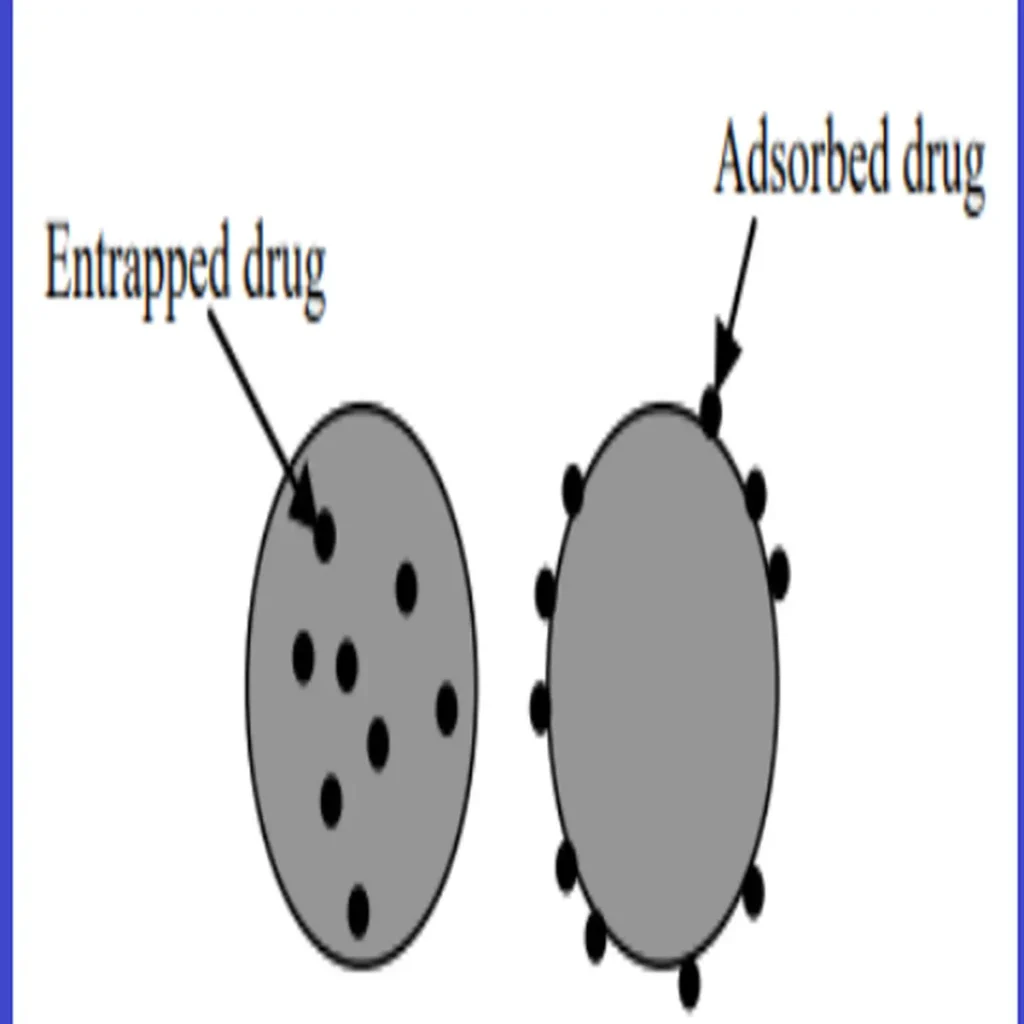
Microcapsules are the enclosed substance is surrounded by a distinct capsule wall. Micromatrices are the substance is spread throughout the matrix. Often, microspheres are termed as microparticles.
Researchers and manufacturers use various natural and synthetic materials to produce microspheres. These materials commonly enhance the effectiveness of traditional drugs while reducing side effects.
Characteristics of ideal microsphere
- It should be able to incorporate a high concentration of drug.
- The synthesized formulation should have a high stability and a clinically acceptable shelf-life.
- It should have a controlled particle size.
- It should have a controlled dispersibility in aqueous vehicles for injection.
- The drug should be release with a good control over a wide time scale.
- It should have biocompatibility with a controlled biodegradability.
- It should be susceptible to chemical modification.
What are the types of microspheres?
Here are 5 main types, bioadhesive microspheres, magnetic, floating, radioactive and polymeric microspheres.
What are bioadhesive microsphere?
These are designed to stick to mucosal membranes such as, the buccal (inside the cheek), ocular (eye), rectal, nasal and more.
They adhere to these surfaces for an extended period, ensuring intimate contact with the absorption site. This prolonged contact enhances the therapeutic action of the medication and make it more effective.
What are magnetic microspheres?
These are used when precise drug localization is crucial. In this drug delivery system, a small amount of medication is magnetically targeted to a specific area, replacing the need for large quantities of freely circulating drugs.
This microsphere contains materials like chitosan and dextran that respond to magnetic fields. There are two main types of magnetic microspheres, therapeutic magnetic microsphere and diagnostic microsphere.
What is therapeutic magnetic microsphere?
It is used to deliver chemotherapeutic agents to liver tumors and can also target proteins and peptides.
What is diagnostic microsphere?
This microsphere serves diagnostic purposes, such as imaging liver metastases or distinguishing bowel loops from other abdominal structures by using nano-sized superparamagnetic iron oxide particles.
What are floating microspheres?
These have lower density than gastric fluid, allowing them to float in the stomach without affecting gastric emptying.
They release medication gradually. They also maintain plasma levels, reduce dose dumping risk and extending therapeutic effects, like delivering ketoprofen.
What are radioactive microspheres?
These are tiny, typically in the range of 10-30nm, which is larger than the diameter of capillaries. These are used in radioembolization therapy to target tumors with radiation.
They stay inside the microspheres and don’t harm healthy tissues. There are different types based on the type of radiation they emit such as, α emitters, β emitters and γ emitters.
What are polymeric microspheres?
These can group into two categories, biodegradable and synthetic polymeric microspheres.
Biodegradable polymeric microsphere:
They made from natural polymers like starch. They swell in contact with water and stick to mucous membranes, increasing their residence time.
Drug release in these microspheres depends on polymer concentration, ensuring sustained release. But a challenge is controlling drug loading efficiency in clinical use.
Synthetic polymeric microspheres:
These are used clinically as fillers, embolic particles and drug carriers. They are safe but can move from the injection site and can potentially harms nearby organs.
What are uses of microspheres?
- In pharmacy, microspheres used in controlled drug delivery.
- They enable prolonged drug release.
- Used for targeted drug delivery.
- Improve drug bioavailability.
- Enhance patient compliance with dosing.
- Reduce side effects by controlled release.
- Microspheres encapsulate drugs for oral administration.
- Offer a wide range of pharmaceutical applications.
- Improve drug stability in formulations.
- Used for various drug delivery systems.
What are the advantages?
Here are some advantages of microsphere,
- Controlled drug release for consistent therapy.
- Targeted delivery for reduced side effects.
- Easier patient compliance with less frequent dosing.
- Enhanced bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
- Minimized adverse effects with precise release.
- Versatile use with various drugs and systems.
- Improved drug stability and shelf life.
- Accurate and predictable dosing.
- Less drug wastage and maximizing efficacy.
What are the disadvantages?
- Complex and costly manufacturing.
- Limited drug payload capacity.
- Potential burst release of drugs.
- Challenges in achieving precise size control.
- Formulation complexity.
- Stringent regulatory requirements.
- Limited suitability for certain drugs.
- Variability in properties.
- Require specialized equipment.
- Potential migration and infection risks.
