Learn synthesis of norepinephrine with structure SAR uses and side effects. Chemical formula C8H11NO3 Molecular weight 169.18 g/mol.
What is norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline. It is a neurotransmitter and hormone produced by the adrenal glands and sympathetic nerve terminals in the body.
It plays a crucial role in the body such as regulating blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate.
Norepinephrine acts on adrenergic receptors in various tissues throughout the body, including the heart, blood vessels, lungs and brain. It is also involved in modulating mood, attention and cognitive function in the central nervous system.
Physiochemical properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C8H11NO3 |
| Molecular weight | 169.18 g/mol |
| Melting point | 157-158 °C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes at high temperatures |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, ethanol, and other polar solvents |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder or crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.230 g/cm³ (solid), 1.049 g/mL (liquid) |
| pKa | 8.93 |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions, but may degrade over time |
| Biological function | Neurotransmitter, hormone, and medication |
| Target receptors | Alpha and beta adrenergic receptors |
| Synthesis | Biosynthesis occurs in the adrenal glands and some neurons. |
| Metabolism | Metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) |
| Half-life | Short half-life of a few minutes in the body |
| Medical uses | Used in the treatment of shock, low blood pressure, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) |
Norepinephrine structure
Synthesis of norepinephrine
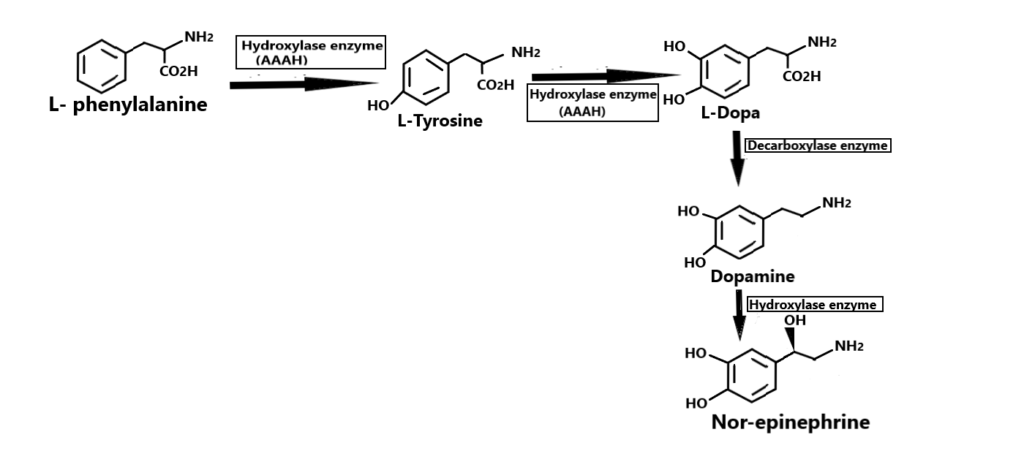
- The amino acid tyrosine is taken up into the chromaffin or sympathetic neuron cells via the amino acid transporter.
- Tyrosine is converted into L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), which requires oxygen and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) as cofactors.
- L-DOPA is then converted into dopamine (DA) by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC).
- DA is transported from the cytoplasm into the synaptic vesicles by the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT).
- Inside the vesicles, DA is converted into NE by the enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH), which requires oxygen, ascorbic acid, and copper as cofactors.
- NE is then stored in the vesicles until it is released in response to a nerve impulse or other stimuli.
What are the uses of norepinephrine?
- Treating low blood pressure in conditions like shock or sepsis.
- Supporting anesthesia during surgery by maintaining blood pressure.
- Assessing cardiovascular function and blood pressure regulation in diagnostic testing.
What are the side effects?
Side effects of norepinephrine may include:
- Tachycardia (increased heart rate).
- Hypertension (rapid increase in blood pressure).
- Extravasation, potentially causing tissue damage.
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), especially in patients with heart conditions.
- Ischemia, which can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Necrosis of peripheral tissues due to prolonged vasoconstriction.
The above uses and side effects of norepinephrine written only for educational purposes. It is important to note that it is a potent medication that requires close monitoring and careful titration by trained medical professionals. The potential benefits and risks of treatment should always be carefully weighed in each individual patient.
Also read Pharmacodynamics: Principle of Drug Action in Pharmacology.
