Learn definition and principle of Quality Risk Management (QRM) with applications. It helps to control risks in pharmaceutical products.
What is Quality Risk Management?
Quality risk management is a systematic way to identify, assess and control risks that may affect the quality of pharmaceutical products.
It involves evaluating potential risks based on scientific knowledge, protecting patients and employing proportional efforts and documentation.
The goal is to implement dynamic and adaptable risk management practices that facilitate continuous improvement and ensure the production of safe and high-quality products.
Principle Quality Risk Management
The principles of quality risk management can be simplified into two main ideas.
- First, the evaluation of risk should be based on scientific knowledge and focused on protecting the patient.
- Second, the level of effort, formalities and documentation in the risk management process should be proportional to the level of risk involved.
In addition to these primary principles, there are two other important principles in risk management.
- The first is that QRM procedures should be dynamic, repetitive and open to change. This means they should be adaptable and flexible.
- The second principle is that the QRM process should include the ability for continuous improvement. This means that the process should always strive to get better over time.
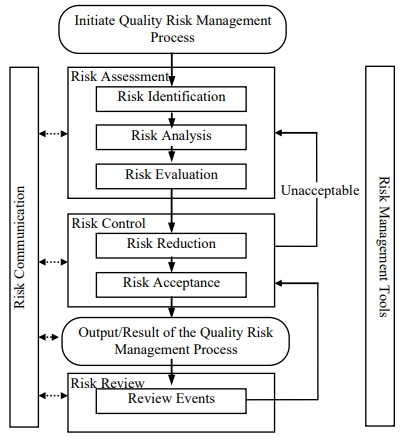
Process
Applications
- QRM is applied in drug development to ensure safety and quality.
- It assesses risks in manufacturing processes to maintain product quality.
- QRM helps in managing risks in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
- It ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
- QRM is used during change control and validation processes.
- It aids in quality control and reliable laboratory operations.
- QRM supports pharmacovigilance and post-market surveillance.
- It is integrated into the overall Quality Management System (QMS).
Some advantages are:
- Enhanced product quality through proactive risk mitigation.
- Science-based decision making grounded in data and evidence.
- Regulatory compliance demonstration.
- Cost savings by focusing resources on critical areas.
- Continuous improvement culture.
- Efficient decision making with a structured framework.
- Increased patient safety through risk assessment and control.
- Collaboration and communication among stakeholders.
- Scalability and adaptability to suit project needs.
- Systematic approach to risk management.
Also read Technology Transfer Protocols in Pharmaceutical Industry.
