Routes of drug administration is way to administrate a drug. It can be classified into local routes and systemic routes.
Routes of drug administration
It is such a path or way by which a drug substance (solid, liquid) is carried for attached with body.
Pharmacology definition, scope, history.
Classification of routes of drug administration
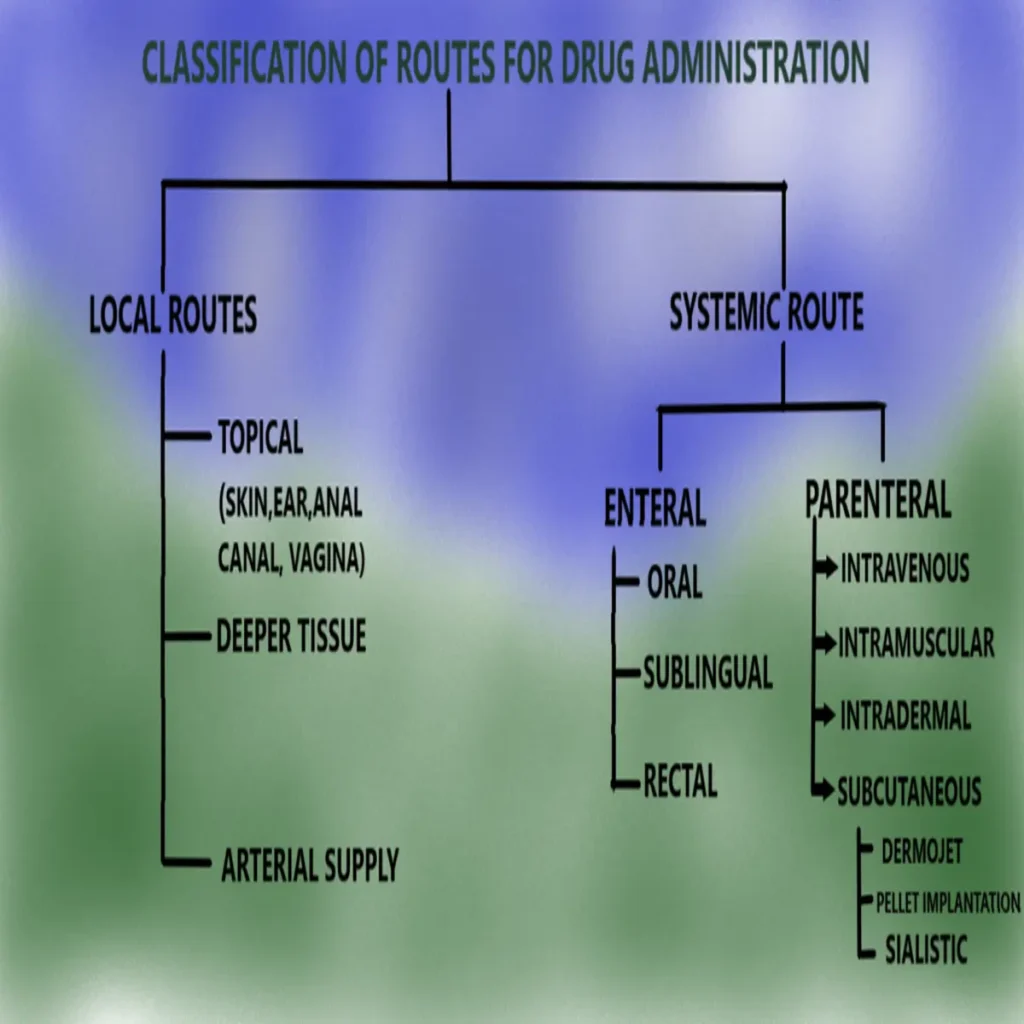
The drug can be administrated through various routes. For administration of drug, appropriate route should be chosen.
Choice of appropriate route depends on situation of patient health and form of drug. Administration routes basically classified into 2 categories – local routes of drug administration and systemic routes of drug administration.
What is local route?
Local route of drug administration refers to the delivery of a drug directly to a specific part of the body For example, like applying cream on the skin, inhaling medicine for the lungs or injecting a drug into a muscle or joint.
What are advantages local routes of drug administration?
- Complete concentration of drug will be available at particular site of body.
- Side effect or toxicity levels are absent or minimal.
- Helpful for patient.
- Drug goes directly delivered to particular site.
What are disadvantages local routes of drug administration?
- Absorption rate will be slow in this route.
- Most of the drugs have poorly lipid soluble.
- Administrated drug can produce skin irritation.
These routes of administration are classified into 3 subcategories – topical route, deeper tissue and arterial supply.
What is topical route?
These routes usually refer the external use of drug to surface wounds.
Topical routes can be eyes, ear, anal canal, vagina, skin surface, oropharyngeal etc.
The drugs delivered in the form of lotion, ointments, cream, suppositories, paints, drops, powder, spray, lozenges, pessaries.
What are advantages of topical route?
- Encourage patient confidence.
- Simply delivered to the localized wounds.
What is deeper tissue administration?
When the drug substances delivered in deep area in body by using a syringe and needles known as deeper tissue administration routes. For example, retrobulbar injection (hydrocortisone acetate injection behind eyeball), Intra-articular injection (Hydrocortisone acetate injection in knee joint due to rheumatoid arthritis).
What is arterial supply in drug administration?
The drug particles injected to artery. For example, introduce anti-cancer drugs into the bronchial artery to localize the effect for limb malignancies.
What is systemic route of drug administration?
The path or way by which drugs absorbed into circular system (blood) and distributed equally to all sites. Systemic routes have 2 main subcategories – enteral and parenteral routes.
What is enteral route?
When drugs or medicine administrated via gastrointestinal tract, known as enteral routes of administration. It includes oral, sublingual and rectal route.
What is oral route of administration?
When the drug administrated through the mouth, known as oral routes of drug administration. This is simple, common and oldest routes of drug administration.
Advantages of oral routes
- Is more convenient and safer.
- It doesn’t need any assistance.
- Painless route of drug administration.
- Solid and liquid dosage can administrate orally.
Disadvantages of oral route
- Drug absorption rate is not accurate, because absorption of drug may not be regular pattern.
- Drug action is slower that’s why oral routes are not suitable during emergencies.
- May causes nausea and vomiting.
- Not useful for unconscious patient.
What is sublingual route?
When the drug substance delivers and kept under tongue, the route is known as sublingual routes.
This route also known as buccal route of administration, because drugs are absorbed by the buccal membrane.
After absorption of drug by buccal membrane the drugs molecules bypass liver and reach to blood circulation. For examples, buprenorphine and glyceryl trinitrate.
Advantages of sublingual drug administration?
- Drug molecules directly reach to blood without involvement of liver.
- Absorption rate is rapid.
- Drug action is too fast.
What are the disadvantages of sublingual routes?
- This route is use only for lipid soluble and non-irritating drugs.
- Not for unconscious patient.
- Duration of drug action is short.
- Taste of drug can be unpleasent.
- Drug interaction with food and drinks, which can reduce the drug action.
What is rectal route?
Administration of drug through rectum called as rectal route of administration.
Administrated drug form can be suppositories (or) enema*. Drug absorbed by the external hemorrhoidal* veins. Examples of drug, Indomethacin and Diazepam etc.
*What is Enema?
Enema is also called as clyster; it is a process in which drug particles (liquid or gas) are injected to rectum by stimulation of evacuation bowl. Enema is use for constipation.
What are the advantages of rectal routes of administration?
- Good to prevent rapid vomiting.
- Good for unconscious patient or those patients not able to swallow.
- Directly absorbed by Hemorrhoidal* veins.
*What is Hemorrhoidal veins?
Hemorrhoidal vein is a one type of swollen vein present in anus and rectum.
What are the disadvantages rectal routes?
- Absorption rate is slower or not regular in pattern.
- Uncomfortable and embarrassing to patients.
- Can create rectal irritation or rectal inflammations.
What is parenteral route of drug administration?
When the drug particle administrated by injection to blood or tissue fluid without crossing enteral mucosa, known as parenteral routes of drug administration. Drug particles reach to its site bypassing the liver.
What are the advantages of parenteral routes of drug administration?
- Drug action is faster than other routes.
- This route is good for emergency or critical condition of patients.
- Doesn’t cause vomiting or gastric Irritation.
- Parenteral routes is useful for unconscious patient.
- Drug cannot interference with food or gastric juice.
What are the disadvantages of parenteral routes?
- Drug may be expensive.
- Can causes pain.
- Chances for local tissue injury.
- Drug preparation has to sterilized.
Parenteral routes are intramuscular, intravenous route and subcutaneous route.
What is intramuscular route of drug administration?
When the drug injected in large skeletal muscle (triceps, gluteus maximus etc.) is known as Intramuscular route.
What are the advantages of Intramuscular route?
- Preparation like oily solution, aqueous suspension can be injected by this route.
- It is less painful than other parenteral routes.
- Mild or moderate irritants can be injected, because large muscles have less sensory nerve.
- Absorption rate of drug is faster.
What are the disadvantages of Intramuscular route?
- Self-injection can be risky because it needed deep penetration.
- Intramuscular route should be avoided for those patients treating by anticoagulant* drug, it can produce side effect like Hematoma*.
*What is Anticoagulant?
Anticoagulants are the drug or medication help coagulation of blood.
*What is Hematoma?
Hematoma is a condition, in which blood will spread out from the blood vessels.
What is intravenous route?
The route, by which drug preparations directly administrated to blood through the veins. Drug preparation is injected as bolus or slowly Infused in superficial veins.
What are the advantages of intravenous route?
- Drug can produce immediate action.
- Great for emergency and critical situation of patient.
- Highly irritants drugs can be injected.
- Response is measurable.
What are the disadvantages of intravenous route?
- Only for aquas solution.
- Can cause air embolism*.
- Riskey for vital organs like heart, brain, kidney.
- Thrombophlebitis can be occurred in injected vein and necrosis of tissue.
Air embolism:
When small amount of air or gases is reach to blood vessels and blocked the vessels known as air embolism. This should treat immediately.
What is subcutaneous route of drug administration?
The drug supplied through injection to the subcutaneous tissues of thigh, abdomen, arm etc. The subcutaneous tissues have more richly nerve.
Drug administration through subcutaneous routes can be done in 2 types – pellet implantation and dermo-jet.
Pellet implantation:
The drug introduced with torcher and cannula in form of solid pellet. This provides slow release over weeks and months.
Dermo-jet:
Without needle, a high velocity of drug solution is transfer from microfine orifice to subcutaneous tissue by using a gun like implement.
The main advantage of dermo-jet route is drug solution passes through the superficial layers and deposited to subcutaneous tissue.
Also read What is pharmacokinetics?
